A hearing test will determine how well an individual can hear and whether the person’s hearing is within the normal range.
During the test, the audiologist will measure the softest level at which an individual can hear a variety of pitches or frequencies that sound like “beeps” during the testing. 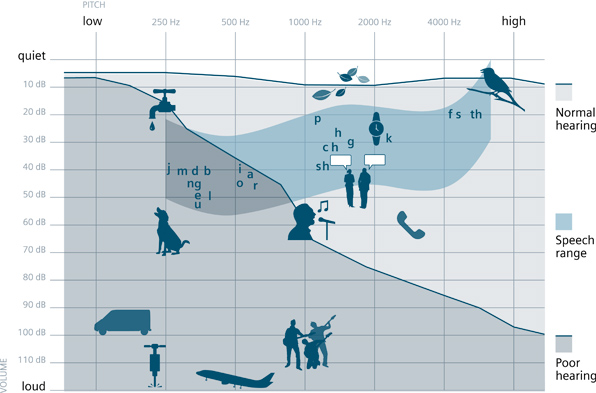
The audiogram is used to document the results of the testing. Think of the audiogram as a picture of an individual’s hearing sensitivity. The audiogram is a graph; the X axis (along the top) shows the frequency in Hertz (Hz). Just as the keys on a piano start with low-pitch sounds on the left moving towards the higher-pitched sounds on the right, the frequencies on the audiogram start with the lower pitched sounds and frequencies and move towards the higher pitched sounds. The number s on the Y axis (left hand side) represent how loud the sounds are res in decibels (Dbs).
When the hearing test is performed, the audiologist records for each frequency the softest level at which the person hears the sounds. This is known as the audiometric threshold. This can be different at each pitch and different for each ear. On the audiogram, you will see that these thresholds are plotted for both the left ear and the right. You will see these marked as symbols X (left ear) and O (right ear).
The shaded areas shown on the graph represent different categories of hearing ability. For example, the area in yellow represents a normal hearing rang while the shaded areas below it represent hearing loss. The further the markings go down the page, the greater the level of hearing loss.
Understand the results
The results of a hearing test give information about each part of the hearing system. If everything appears to be normal for the patients age and medical history or there is little change from the last test, returning in a year or so may be recommended.
If the test shows anything other than normal, the audiologist can recommend the appropriate solution which may include medical referral, communication improvement strategies or amplification.


